What is the difference between a lawyer and an attorney? This question often arises, and understanding the distinction is crucial. While the terms are frequently used interchangeably, there are subtle yet significant differences. Let’s delve into the nuances to gain a clear understanding.
Both lawyers and attorneys possess a Juris Doctor degree and have passed the bar exam, but their roles and responsibilities may vary depending on their jurisdiction and practice area.
Definition and Scope
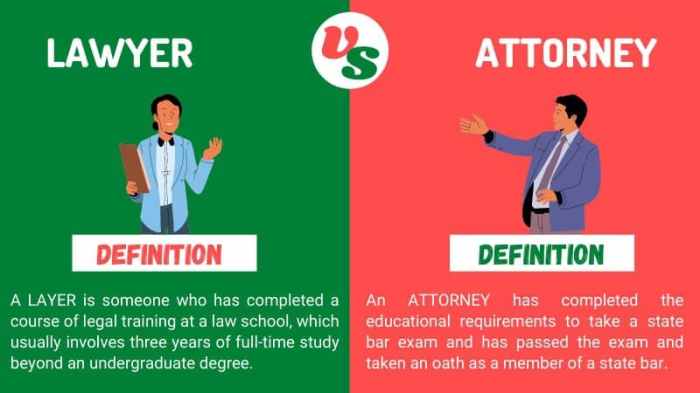
The terms “lawyer” and “attorney” are often used interchangeably, but there are subtle differences between the two. In general, a lawyer is a person who has been trained in the law and is licensed to practice law. An attorney is a lawyer who has been admitted to practice law in a particular jurisdiction.
Both lawyers and attorneys can provide legal advice, represent clients in court, and draft legal documents. However, there are some key differences between the two.
Overlapping Responsibilities and Authorities
One of the key differences between lawyers and attorneys is the scope of their practice. Lawyers are generally licensed to practice law in all areas of law. Attorneys, on the other hand, are only licensed to practice law in the jurisdiction in which they have been admitted.
Another key difference between lawyers and attorneys is the level of their authority. Lawyers are generally authorized to practice law in all courts. Attorneys, on the other hand, are only authorized to practice law in the courts of the jurisdiction in which they have been admitted.
The following table summarizes the key differences between lawyers and attorneys:
| Characteristic | Lawyer | Attorney |
|---|---|---|
| Scope of practice | All areas of law | Only the jurisdiction in which they have been admitted |
| Level of authority | All courts | Only the courts of the jurisdiction in which they have been admitted |
Educational Background
The path to becoming a lawyer or attorney involves a rigorous educational journey that encompasses both academic study and practical training. To embark on this legal profession, aspiring individuals must navigate a comprehensive curriculum that equips them with the knowledge, skills, and ethical foundation essential for success in the field of law.
Law School
Prospective lawyers and attorneys embark on a three-year journey through law school, where they delve into a comprehensive curriculum designed to provide a thorough understanding of the legal system, its principles, and its complexities. The coursework encompasses a wide range of subjects, including constitutional law, criminal law, civil procedure, contracts, torts, and legal writing.
Through a combination of lectures, discussions, and legal analysis, students develop a deep understanding of the legal framework and the critical thinking skills necessary to navigate its intricacies.
Licensing and Regulation: What Is The Difference Between A Lawyer And An Attorney
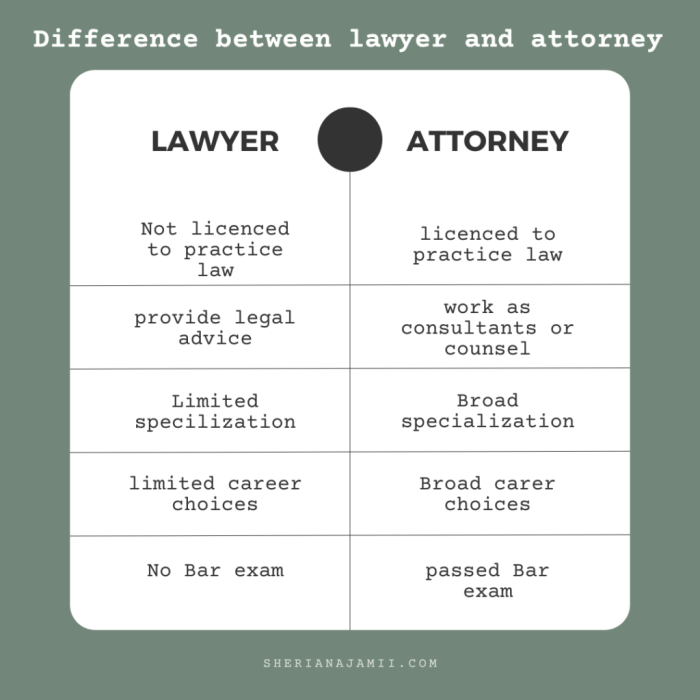
The licensing and regulation of lawyers and attorneys vary across jurisdictions, ensuring that they meet the necessary qualifications and ethical standards to practice law. These regulations include licensing processes, continuing legal education requirements, pro bono work requirements, and disciplinary procedures.
Licensing Processes
- United States:Requires a Juris Doctor (J.D.) degree from an accredited law school and passing the bar exam in the state where they wish to practice.
- United Kingdom:Requires a qualifying law degree (LL.B.) and passing the Legal Practice Course (LPC) or Bar Professional Training Course (BPTC).
- European Union:Allows lawyers licensed in one EU member state to practice in other member states under the European Union’s Mutual Recognition of Professional Qualifications Directive.
Continuing Legal Education Requirements
Most jurisdictions require lawyers and attorneys to complete continuing legal education (CLE) courses to stay up-to-date on legal developments and maintain their knowledge.
Pro Bono Work Requirements
Some jurisdictions have pro bono work requirements for lawyers and attorneys, mandating that they provide a certain number of hours of free legal services to those in need.
Disciplinary Procedures
All jurisdictions have disciplinary procedures in place to address complaints of misconduct by lawyers and attorneys. These procedures typically involve investigations, hearings, and potential sanctions, including disbarment.
Ethical Responsibilities
Lawyers and attorneys have ethical responsibilities to uphold, including:
- Confidentiality:Maintaining the confidentiality of client communications and information.
- Conflict of Interest:Avoiding conflicts of interest that could impair their ability to represent clients effectively.
- Competence:Providing competent legal services and not taking on cases where they lack the necessary knowledge or experience.
Resources for Lawyers and Attorneys
- American Bar Association (ABA)
- Law Society of England and Wales
- International Bar Association (IBA)
Areas of Practice
Lawyers and attorneys cover a diverse range of legal disciplines, each requiring specialized knowledge and skills. They focus on specific areas of law, providing legal counsel, representation, and advocacy to their clients.
The following table Artikels some of the common areas of law that lawyers and attorneys specialize in, along with examples of legal services offered within each area:
Civil Litigation
- Represent clients in civil lawsuits involving disputes between individuals, businesses, or organizations
- Handle matters such as breach of contract, personal injury, property disputes, and family law issues
Criminal Defense
- Represent individuals accused of crimes
- Provide legal counsel, defend clients in court, and negotiate plea agreements
Corporate Law
- Advise businesses on legal matters, including mergers and acquisitions, corporate governance, and regulatory compliance
- Draft and review contracts, negotiate agreements, and represent clients in business disputes
Estate Planning
- Assist individuals with creating wills, trusts, and other estate planning documents
- Provide guidance on tax implications, probate administration, and asset distribution
Family Law
- Represent clients in family law matters, such as divorce, child custody, and support
- Negotiate settlements, draft legal documents, and advocate for clients’ rights
Immigration Law
- Assist individuals and businesses with immigration-related matters, including visas, green cards, and citizenship applications
- Provide legal counsel, represent clients in immigration proceedings, and advocate for their rights
Intellectual Property Law
- Protect and enforce intellectual property rights, such as patents, trademarks, and copyrights
- Draft and review intellectual property agreements, negotiate licenses, and represent clients in infringement disputes
Real Estate Law
- Handle real estate transactions, including buying, selling, and leasing property
- Draft and review contracts, negotiate terms, and represent clients in real estate disputes
Tax Law
- Advise individuals and businesses on tax matters, including tax planning, tax compliance, and tax disputes
- Prepare tax returns, represent clients in tax audits, and negotiate with tax authorities
Career Paths
After completing their education and passing the bar exam, lawyers and attorneys embark on diverse career paths. Their progression within the legal profession depends on their skills, experience, and aspirations.
Roles and Advancements
- Associate Attorney:Entry-level position in law firms, where lawyers assist senior attorneys with research, drafting, and other legal tasks.
- Junior Partner:Lawyers who have demonstrated exceptional abilities and experience may be promoted to junior partner, sharing in the firm’s profits and responsibilities.
- Senior Partner:Experienced lawyers who have made significant contributions to the firm’s success and reputation.
- Of Counsel:Lawyers who work independently but have an ongoing relationship with a law firm, providing expertise and support.
- In-House Counsel:Lawyers employed by corporations or other organizations to provide legal advice and representation.
- Public Defender:Lawyers who represent individuals who cannot afford private counsel.
- Prosecutor:Lawyers who represent the government in criminal cases.
- Judge:Lawyers who preside over court proceedings and make legal decisions.
Client Representation
In the legal realm, attorneys and lawyers serve as advocates and counselors for their clients, navigating the complexities of the legal system on their behalf. They assume the critical responsibility of representing individuals and organizations, safeguarding their rights, and pursuing their interests.
Ethical Responsibilities and Conflicts of Interest
Attorneys are bound by strict ethical guidelines that govern their conduct and interactions with clients. These ethical responsibilities include maintaining client confidentiality, avoiding conflicts of interest, and acting with integrity and fairness. Conflicts of interest arise when an attorney’s personal or financial interests could potentially compromise their ability to represent a client effectively.
In such situations, attorneys are obligated to disclose the conflict and take appropriate steps to address it.
Attorney-Client Privilege
The attorney-client privilege is a fundamental legal principle that protects the confidentiality of communications between an attorney and their client. This privilege is essential for fostering trust and open communication, enabling clients to disclose sensitive information without fear of its disclosure to third parties.
However, the privilege has certain limitations, such as when the client intends to commit a crime or fraud.
Types of Legal Representation
Attorneys offer a range of legal representation services tailored to the specific needs of their clients. Pro bono representation involves providing legal services to individuals or organizations who cannot afford to pay, often through non-profit organizations or legal aid clinics.
Contingency fees are another common arrangement, where attorneys receive payment only if they successfully resolve a case in favor of their client.
Client Confidentiality and Attorney-Client Communication
Client confidentiality is paramount in the attorney-client relationship. Attorneys are ethically and legally obligated to keep their clients’ information confidential, even after the representation has ended. Open and effective communication between attorney and client is crucial for developing a successful strategy and achieving the desired outcome.
Ethical Dilemmas in Client Representation
Attorneys often face complex ethical dilemmas in their representation of clients. These dilemmas can arise from conflicts of interest, client requests for illegal or unethical actions, or situations where the attorney’s personal beliefs conflict with their client’s interests. Navigating these ethical challenges requires careful consideration of legal obligations, professional standards, and the attorney’s own moral compass.
Advocacy and Litigation
Lawyers and attorneys play a crucial role in advocating for their clients’ rights and interests in court proceedings. They present arguments, examine witnesses, and develop legal strategies to achieve favorable outcomes for their clients.
Courtroom Procedures, What is the difference between a lawyer and an attorney
In a courtroom setting, lawyers and attorneys must adhere to specific procedures and protocols. They must present their cases in a logical and persuasive manner, following the rules of evidence and court decorum. They also engage in cross-examination, where they question the opposing party’s witnesses to challenge their testimony and uncover inconsistencies.
Legal Strategies
Lawyers and attorneys employ various legal strategies to advocate for their clients. These strategies may include:
Negotiation
Attempting to resolve disputes outside of court through discussions and compromise.
Mediation
Utilizing a neutral third party to facilitate communication and find common ground between the parties.
Litigation
Pursuing a case through the court system, presenting evidence and arguments to support their client’s position.
Legal Advice and Counseling
Lawyers and attorneys play a crucial role in providing legal advice and counseling to their clients. They use their knowledge of the law to help individuals and organizations understand their legal rights and obligations. Lawyers and attorneys can provide guidance on a wide range of legal matters, including contracts, property law, family law, and criminal defense.
Confidentiality and Informed Decision-Making
One of the most important aspects of the attorney-client relationship is confidentiality. Lawyers and attorneys are required to keep all communications with their clients confidential, which means they cannot disclose any information about their clients or their cases to anyone else without their consent.
This privilege is essential for clients to feel comfortable discussing their legal problems with their lawyers and attorneys and to make informed decisions about their cases.
Negotiation and Dispute Resolution
Lawyers and attorneys play a crucial role in negotiating and resolving disputes. They assist clients in finding amicable solutions, avoiding protracted legal battles, and preserving relationships.
Alternative dispute resolution (ADR) methods offer alternatives to traditional litigation, promoting efficiency and confidentiality. These methods include:
Mediation
Mediation involves a neutral third party facilitating communication between disputing parties. The mediator helps parties identify common ground, explore options, and reach mutually acceptable agreements.
Arbitration
Arbitration involves a neutral third party (arbitrator) hearing evidence and arguments from both parties. The arbitrator makes a binding decision that is typically final and enforceable by law.
Negotiation
Negotiation involves direct communication between parties, with or without the assistance of a lawyer or mediator. Parties engage in discussions to reach a mutually agreeable outcome.
Conciliation
Conciliation involves a neutral third party (conciliator) assisting parties in identifying issues, exploring solutions, and facilitating an agreement. Unlike mediation, the conciliator may offer suggestions or recommendations.
Advantages and Disadvantages of ADR Methods
Each ADR method has its advantages and disadvantages:
- Mediation:Advantages include confidentiality, flexibility, and the potential for preserving relationships. Disadvantages include the lack of binding outcomes and the possibility of impasse.
- Arbitration:Advantages include speed, confidentiality, and the finality of decisions. Disadvantages include the cost, the potential for bias, and the limited scope for appeal.
- Negotiation:Advantages include direct communication, flexibility, and the potential for creative solutions. Disadvantages include the potential for power imbalances and the lack of third-party oversight.
- Conciliation:Advantages include the involvement of a neutral third party, the potential for comprehensive solutions, and the flexibility of the process. Disadvantages include the potential for delay and the possibility of impasse.
Examples of ADR in Practice
- Mediation:Used in family disputes, workplace conflicts, and community disputes.
- Arbitration:Used in commercial contracts, construction disputes, and international trade disputes.
- Negotiation:Used in business deals, contract negotiations, and personal injury settlements.
- Conciliation:Used in labor disputes, environmental disputes, and international conflicts.
Ethical Considerations in Negotiation and Dispute Resolution
Lawyers and attorneys have ethical obligations in negotiation and dispute resolution, including:
- Maintaining confidentiality
- Avoiding conflicts of interest
- Acting in the best interests of their clients
- Promoting fair and equitable outcomes
- Adhering to professional standards
Fees and Billing Practices
Lawyers and attorneys typically charge fees for their services, and these fees can vary depending on a number of factors. Some of the most common fee structures include hourly billing, flat fees, and contingency fees.
Hourly billing is the most common fee structure, and it involves the lawyer or attorney charging a set hourly rate for their time. The rate can vary depending on the lawyer’s experience, expertise, and location. Flat fees are another common fee structure, and they involve the lawyer or attorney charging a fixed fee for a specific service.
This type of fee structure is often used for simple legal matters, such as drafting a will or reviewing a contract.
Contingency fees are a type of fee structure in which the lawyer or attorney only gets paid if they are successful in winning the case. This type of fee structure is often used in personal injury cases, where the lawyer or attorney takes a percentage of the settlement or award.
Factors that Influence Legal Fees
There are a number of factors that can influence legal fees, including:
- The complexity of the case
- The experience of the lawyer or attorney
- The location of the lawyer or attorney
- The type of fee structure
It is important to discuss fees with your lawyer or attorney before hiring them so that you understand the costs involved.
Ethical Considerations
There are a number of ethical considerations that lawyers and attorneys must follow when it comes to fees and billing practices. These considerations include:
- Lawyers and attorneys must be transparent about their fees.
- Lawyers and attorneys must not charge excessive fees.
- Lawyers and attorneys must not enter into contingency fee agreements that are not in the best interests of their clients.
Best Practices for Clients
When it comes to understanding and negotiating legal fees, there are a number of best practices that clients can follow:
- Get a written fee agreement before hiring a lawyer or attorney.
- Negotiate the fees if you are not comfortable with the initial quote.
- Ask for a detailed explanation of the fees and billing practices.
- Keep track of your legal expenses.
By following these best practices, clients can help ensure that they are getting the best possible value for their legal services.
Professional Organizations and Associations
Lawyers and attorneys can join professional organizations and associations to connect with peers, stay informed about legal developments, and enhance their professional skills. These organizations offer various benefits and resources to their members.
One of the most prominent organizations for lawyers is the American Bar Association (ABA). The ABA provides continuing legal education programs, networking opportunities, and advocacy for the legal profession. Other notable organizations include the National Bar Association (NBA), which represents the interests of African American attorneys, and the Hispanic National Bar Association (HNBA), which serves the Hispanic legal community.
Benefits of Professional Organizations
- Continuing Legal Education (CLE): These organizations offer CLE courses to help lawyers stay up-to-date on legal developments and earn CLE credits required for maintaining their licenses.
- Networking Opportunities: Professional organizations provide platforms for lawyers to connect with other attorneys, judges, and legal professionals, fostering collaboration and building professional relationships.
- Advocacy and Representation: These organizations advocate for the legal profession and represent the interests of their members before legislative bodies and other decision-makers.
- Publications and Resources: Professional organizations publish journals, newsletters, and other resources that provide valuable information on legal trends, case law, and best practices.
- Ethics and Professionalism: These organizations promote ethical conduct and professional standards within the legal profession, providing guidance and support to members.
Public Perception and Stereotypes

The public perception of lawyers and attorneys is often shaped by stereotypes and misconceptions. Some common stereotypes include the portrayal of lawyers as greedy, manipulative, and only interested in making money. However, these stereotypes are far from the truth.Lawyers play a vital role in society, providing legal advice, representing clients in court, and advocating for justice.
They are essential to the functioning of our legal system and help ensure that everyone has access to justice, regardless of their background or financial situation.
Challenging Common Misconceptions
It is important to challenge the common misconceptions and stereotypes about lawyers. By educating the public about the true nature of legal work, we can help to create a more accurate and informed understanding of the profession.Here are some of the most common stereotypes about lawyers, along with a brief explanation of why they are inaccurate:
- Lawyers are only interested in making money.While it is true that lawyers charge for their services, they are not motivated solely by financial gain. Many lawyers are passionate about helping others and making a positive impact on the world.
- Lawyers are dishonest and manipulative.This is a harmful stereotype that is simply not true. The vast majority of lawyers are honest and ethical individuals who are committed to upholding the law.
- Lawyers are only good at arguing.While lawyers do need to be able to argue effectively, they also need to be able to negotiate, write, and research. They need to be able to think critically and solve problems. Lawyers use their skills to help their clients achieve their goals, whether that is winning a case in court or negotiating a settlement.
It is important to remember that lawyers are people too. They have their own strengths and weaknesses, just like everyone else. Some lawyers may be more aggressive than others, while some may be more analytical. It is important to find a lawyer who is a good fit for your personality and needs.
Emerging Trends and Future Prospects

The legal profession is constantly evolving, with emerging trends and advancements shaping the roles of lawyers and attorneys. These trends include the rise of artificial intelligence (AI), legal technology, globalization, data privacy, and cybersecurity.
AI is transforming the legal industry by automating tasks, providing predictive analytics, and enhancing decision-making. Legal tech is also streamlining legal processes, improving productivity, and reducing errors. Globalization is increasing the demand for lawyers with international expertise and leading to the harmonization of laws.
Data Privacy and Cybersecurity
Concerns over data protection, privacy breaches, and cybercrime are creating new legal challenges and increasing the demand for specialized lawyers. Ethical considerations in the legal profession are also evolving as technology advances.
Ethical Considerations in the Legal Profession
“As technology advances and the legal landscape evolves, it is crucial to address the ethical implications of emerging trends. Lawyers must navigate the challenges of data privacy, algorithmic bias, and the potential impact of AI on the justice system.”
Emerging Legal Specializations
Emerging legal specializations include AI law, data privacy law, cybersecurity law, and international law. These specializations reflect the changing needs of society and the challenges of the 21st century.
Future Trajectory of the Legal Profession
The legal profession is expected to continue to evolve in the future, with technology playing an increasingly important role. Lawyers and attorneys will need to adapt to the changing landscape and embrace emerging trends to remain competitive and provide effective legal services.
Final Conclusion
In essence, lawyers and attorneys are legal professionals who provide guidance and representation in various legal matters. Their expertise enables them to navigate the complexities of the legal system and protect the rights and interests of their clients.
FAQ Corner
What is the primary role of a lawyer?
Lawyers provide legal advice, represent clients in court, and draft legal documents.
What is the difference between a lawyer and a solicitor?
In some jurisdictions, such as the United Kingdom, the term “solicitor” refers to a lawyer who deals with non-contentious legal matters, while “barrister” refers to a lawyer who represents clients in court.
Can a lawyer practice law in any state?
No, lawyers are generally licensed to practice law only in the state where they have passed the bar exam.